General
|
General Information |
The 8085 was the follow-on processor to the very successful Intel 8080A processor. The 8085 got its name because it was Intel’s first 5 volt microprocessor. The 8085 was 100% software compatible with the 8080A with increased systems performance. The initial 8085’s were based on NMOS technology and the later “H” versions were based on HMOS technology. The 8085 incorporated all the features of the 8224 (clock generator) and the 8228 (system controller) increasing the level of system integration. The 8085 along with and 8156 RAM and 8355/8755 ROM/PROM constituted a complete system. The 8085 used a multiplexed Data Bus and required the 825X-5 support chips. The address was split between the 8-bit address bus and 8-bit data bus. The on-chip address latch of 8155/8355/8755 memory chips allowed a direct interface with the 8085. The 8085 family is also referred to as the MCS-85. |
|
Production |
April, 1976 |
| Designers | Unknown |
Architecture
| Type | Data Word | Address Space | Clock | Instruct- ions | Assists | Reg’s GP | Reg’s Math | Reg’s Index | IO Ports | Stack | Interrupts | Memory |
| NMOS & HMOS,CPU
|
8-bit | 64KB | Base 3Mhz, (-2) 5Mhz, (-1) 6Mhz | 48 | Ext* | 0 | 1 | 6 8-bit | NA | NA | 4 Vectors | NA |
* Intel made a hardware multiply chip called the 8231 for the 8080/85
Standard Packages
Modified Packages (I, M, L, and Q)
|
Chip Name |
Package |
On-Chip Identification |
Picture |
General Comments |
|
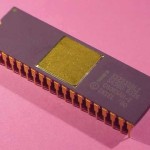
ID8085AH |
Gray Ceramic, 40-pin DIP |
ID8085AH |
 |
Related Chips
|
Related Chips |
Intel 8080 |
|
Second Sources |
AMD, National Semiconductor, Mitsubishi, Toshiba, NEC, Siemens |
| Support Chips | 8155 (2048-bit static MOS RAM with I/O Ports and Timer, CE Active Low), 8156 (Same 8155, but CE Active High), 8355 (16,384-bit ROM with I/O), 8755 (16,384-bit EPROM with I/O), 8251A (Programmable Communications Interface), 8253-5 (Programmable Interval Timer), 8255-5 (Programmable Peripheral Interface), 8257-5 (DMA Controller), 8259-5 (Interrupt Controller), 8279-5 (Keyboard/Display Interface) |